This is an online platform of Terri, an English teacher to share her teaching ideas resources, and some thoughts.
9/26/2009
Richael's Rocket
Does Rachael ride a rocket to Rome on a race?
If Rachael rides a rocket to Rome on a race,
where is the rocket Rachael rides?
Rachael rode a rocket to Rome on a race.
Did Rachael ride a rocket to Rome on a race?
If Rachael rode a rocket to Rome on a race,
where was the rocket Rachael rode?
Rachael will ride a rocket to Rome on a race.
Will Rachael ride a rocket to Rome on a race?
If Rachael rides a rocket to Rome on a race,
where will be the rocket Rachael rides?
9/19/2009
Synonym and Antonym
The leading causes of amnesia健忘症 are either physical or psychological.
In antergrade amnesia, the subject is unable to recall the events that occur after a shock or an injury to the brain; however, past memories will not be lost.
In retrograde amnesia, the patient is capable of recalling events that occur after the trauma; interestingly enough, the information stored before the shock, is lost and cannot be retrieved.
In paraamnesia, established memories are contorted. In psychogenic fugue, the subject may venture into a new lifestyle, trying to repress memories which lead to trepidation. The events happening during psychogenic fugue are non-retrievable. Nonetheless, the experiences that happened before the onset can be recovered.
1. What is the topic of the passage?
2.What are the synonyms or antonym of the following words you will find in the passage.
a. subject ________________________
b. injury ________________________
c. amnesia _______________________
d. unable ________________________
e. happen ________________________
f. however _______________________
The Knight
The knave needed a new knife.
The knife was near the knight's knee.
The knight needed the knife for the night.
The knight knew the knife's name.
The knight named the knife the knight.
Can you identify the homonym words?
Be careful! when you read, make sure you do not add the k-sound before the "kn" words.
9/12/2009
Synonym and Homonym
joyful, merry, happy.
- I wish you a happy birthday.
- I wish you a merry Christmas.
- I wish you a joyful vacation.
Sentence, Sentence
The former president of Taiwan was sentenced to life in prison.
He wrote long sentences to the court.
Life, Life
Life is beautiful and created by God.
Mr Chen would spend his life time in prison.
Homonym 同字異義

sentence (句子, 判決)
The former president, Chen Shui Bian was sentenced to life in prison yesterday.
This is a long sentence.
life (終身, 生命)
life is the experience of being alive.
The judges sentenced Mr Chen to life in prison.
charge, charge
I charge my students $XXX per lesson.
The Taiwan ex-president was convicted of a total of six charges.
fine, fine
I am fine, thank you.
The ex-president was fined $6 millions.
demonstrate, demonstrate
I use the power point to demonstrate the findings.
The supporters of Mr Chen demonstrated near the court.
frequent, frequent
He likes to frequent the bar.
Mr Chen frequently clashed with Chinese leaders by asserting Taiwan's independence.
9/11/2009
Homonym Words
left, left (左,離開)
row, row (一列, 划船)
bear, bear (熊,承受)
Shirley and Karen were good friends. They always sat together on the first row of their classroom. They left school and worked for a Teddy Bear House in Tsim Sha Tsiu when they were sixteen. Shirley wrote with her left hand but rowed boat with her right hand. Karen wrote and rowed with her right hand. Both of them have their own boats which could bear heavy loads.
Homonymy of English Words
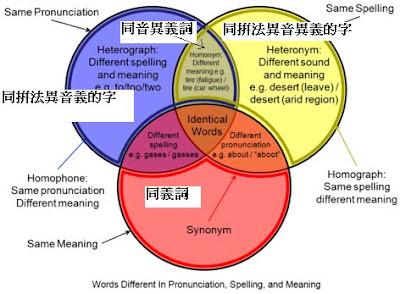
homonym 同音異義詞
Homonyms are words that are pronounced or spelled the same way but have different meanings since they come from different origins. Homonymy is the state of being homonym.
Examples of homonyms are stalk (which as a noun can mean part of a plant, and, as a verb, to follow/harass a person), bear (animal) and bear (carry), left (opposite of right) and left (past tense of leave). Some sources also consider the following trio of words to be homonyms, but others designate them as "only" homophones: to, too and two (actually, to, to, too, too and two, being "for the purpose of" as in "to make it easier", the opposite of "from", also, excessively, and "two", respectively).
Extracted and adapted from Wikipedia at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homonym
19 Life Skills
Skill 1 - Share Joy
Mutual amplification of joy through nonverbal facial expressions and voice tone conveys, “We are glad to be together.” This capacity allows us to bond and grow strong brains as well.
Skill 2 - Soothe Ourself
Lowering the energy level so we can rest after both joyful and upsetting emotions, as we need to and on our own, makes us feel stable. This self-soothing capacity is the strongest predictor of good mental health for the lifetime.
Skill 3 -Form Bonds for Two
The essence of a secure bond is the ability to synchronize our attachment centers so that we can move closer or farther apart at moments that satisfy us both. Synchronized attachment centers provide the basis for smooth transfer of brain skills and learned characteristics.
Skill 4 - Create Appreciation
High levels of the emotional state of appreciation closely match the healthy balanced state of the brain and nervous system. Creating a strong feeling of appreciation in yourself or others relieves unpleasant states and stress. Appreciation is very similar to the let down reflex that produces milk flow when nursing and the warm contented feeling that follows for mother and child.
Skill 5 - Form Family Bonds
Family bonds allow us to feel joy when we have a good relationship with each other. We experience what they feel and understand how they see.
Skill 6 - Identify Heart Values From Suffering
Everyone has issues that particularly hurt or bother him/her and always have been the way he/she is likely to get hurt. Looking at these lifelong issues helps identify the core values for each person’s unique identity. We hurt more as we care more. Because of how much pain our deepest values have caused, most people see these characteristics as liabilities not treasures.
Skill 7 - Tell Synchronized Stories
When our brain is well trained, our capacity is high and we are not triggered by the past, our whole brain works together. Telling stories in a way that requires all the brain to work together is a simple test of how our brain is working as well as a method to train the brain.
Skill 8 - Identify Maturity Levels
We need to know our ideal maturity level so we know if our development is impaired. Knowing our immediate maturity level from moment to moment lets us know if we have been triggered into reactivity by something that just happened or have encountered a “hole” in our development that needs remedial attention. Watching when our maturity level is slipping also tells us when emotional capacity has been drained in us or others.
Skill 9 - Take a Breather
Sustained closeness and trust requires us to stop and rest before people become overwhelmed and when they are tired. These short pauses to quiet and recharge take only seconds. Those who read the nonverbal cues and let others rest are rewarded with trust and love.
Skill 10 - Tell Nonverbal Stories
When we want to strengthen relationships, resolve conflicts, bridge generations or cultures we get much farther with the nonverbal parts of our stories than with words.
Skill 11 - Return to Joy from the Big Six Feelings
Although we live most of our lives in joy and peace we need to learn how to stay in relationship and quiet our distress when things go wrong. When we take good care of our relationships, even when we are upset, the upset does not last long or drive people away. We quickly resolve our “not glad to be together” moments.
Skill 12 - Recall the harmonious moment
Part of maintaining our relationships when we are upset is learning to act like the same person we were when we had joy to be together. A lack of training or bad examples causes us to damage or withdraw from the relationships we value when we get angry, afraid, sad, disgusted, ashamed or hopeless.
Skill 13 - See What God Sees
Hope and direction come from seeing situations, ourselves and others they way they were meant to be instead of only seeing what went wrong. This spiritual vision guides our training and restoration. Even forgiveness flows from seeing people’s purpose as more important than their malfunctions and makes us a restorative community instead of an accusing one. Through our hearts we see the spiritual vision God sees.
Skill 14 - Stop the Sark
This Greek word (also rendered sarx) refers to seeing life according to our view of who people are and how things should be. This conviction, that I know or can determine the right thing to do or be, is the opposite of heartsight in skill 13. For the sark, people become what they have done (the sum of their mistakes) or what we want them to become for us. Blame, accusations, condemnation, gossip, resentment, legalism, self-justification and self-righteousness are signs of the sark.
Skill 15 - Quiet Interactively
Facial cues, particularly of fear, help us to know when we are pushing others too hard. Sometimes we need and want to maintain a high-energy state without “going over the top,” like knowing when to stop tickling so it stays fun. Fast recognition and response to facial cues means optimum interactions and energy.
Skill 16 - Recognize High and Low Energy Response Styles
Many characteristic responses to emotions and relationships are strongly shaped by our tendency toward high or low energy reactions. Recognizing who tends to respond with high energy (adrenalin based emotions) and who would rather withdraw helps us match minds with others and bring more helpful variety to our own response tendencies.
Skill 17 - Identify Attachment Styles
How well we synchronize our attachments (Skill 3) early in life leaves the most enduring pattern in our personality. These patterns change the way we experience reality. At one end we may give almost no importance to our feelings or relationships and at the other we may feel hurt almost constantly and think of nothing but feelings and people. We may also become afraid of the very people we need. All these factors distort our reality but feel real to us at the time. Knowing how to spot these distortions helps us compensate.
Skill 18 - Intervene Where the Brain is Stuck
By recognizing the characteristic pain at each of the brain’s five levels we can pinpoint trouble and find a solution if someone gets stuck. The type of pain gives us a good idea of the kind of solution we will need when someone is not “keeping it together,” “falling apart,” or “stuck” as we commonly call these losses of synchronization.
Skill 19 - Recover From Complex Emotions
Once we can return to joy and act like ourselves with the six big negative feelings taken one at a time, we can begin to learn how to return to joy and act like ourselves when the six are combined in various combinations. Shame and anger combine to form humiliation. Fear and hopelessness (with almost any other feeling as well) form dread. These combination feelings can be very draining and difficult to quiet.
-
It's awesome... Wisdom is presented metaphorically 以隱喻方式 in the article as a guide, protector, and friend. He can lead, keep, and talk w...
-
Beethoven Symphony No. 5 (貝多芬第五交響曲) The coversheet to Beethoven's 5th Symphony The dedication to Prince J. F. M. Lobkowitz and Count Ra...
-
Conditional Sentences - Type 0 Type 0 conditionals are used to express a general truth or a scientific fact. In this type of conditional we ...

